When it comes to precise medical coding, Gout ICD 10 documentation is critical for both clinical accuracy and smooth claims processing. Gout, a painful inflammatory arthritis caused by uric acid buildup, affects millions in the U.S., often requiring consistent diagnosis coding. Whether you’re a provider or part of a medical billing company, like Precision Hub, which offers expert medical billing services, accurate coding using ICD-10 is essential for compliance, reimbursements, and quality care delivery.
Understanding Gout in ICD-10
The International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10), categorizes Gout ICD 10 under the code family “M10.” Each subtype reflects different causes or manifestations of gout, which helps healthcare professionals capture diagnostic specificity.
Main Code: M10 – Gout
This general code is often not billable on its own unless specificity is not available. Instead, providers are encouraged to code one of the subcategories below:
Types of Gout and Their ICD-10 Codes
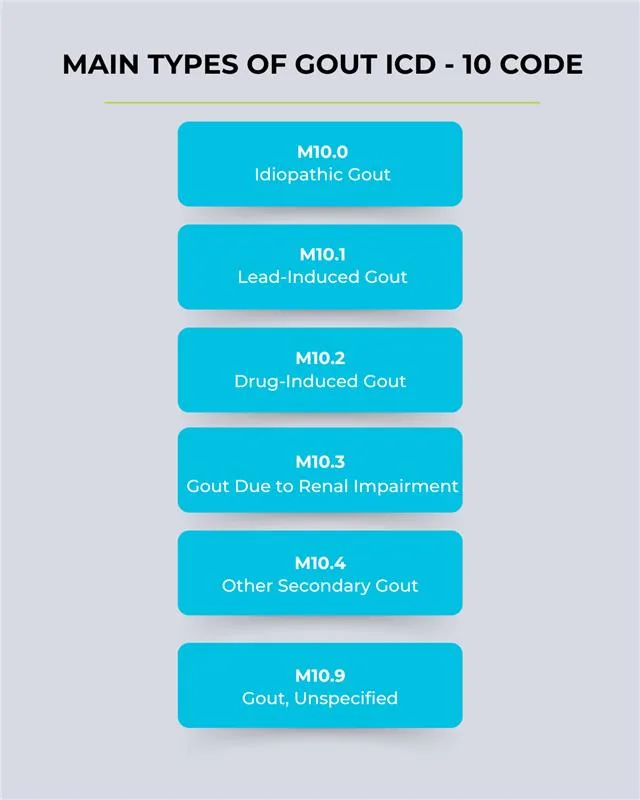
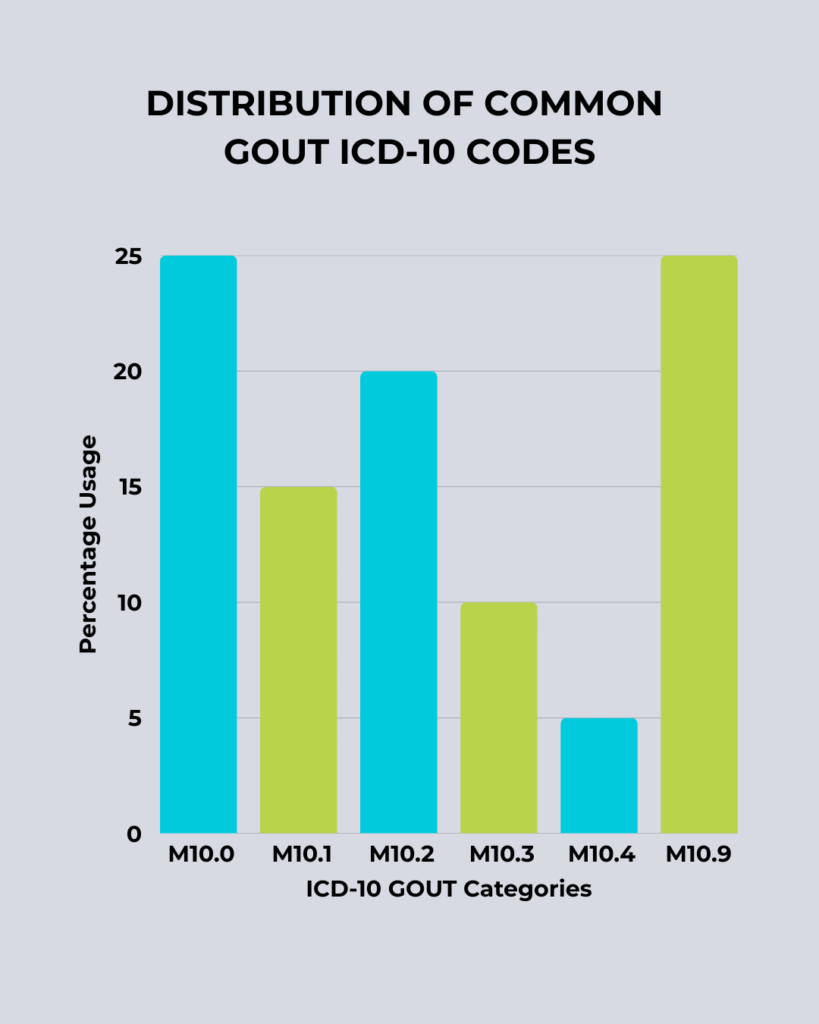
Each code requires details like affected joint, laterality, and acute or chronic nature to ensure billing accuracy.
Causes and Risk Factors for Gout
Gout isn’t random, has known triggers and associations:
- High Uric Acid Levels – Diets rich in red meat, alcohol, and seafood
- Kidney Dysfunction – Limits uric acid elimination
- Genetic Predisposition – Family history of gout
- Medications – Diuretics, aspirin, and some anti-rejection drugs
- Other Conditions – Hypertension, obesity, and diabetes
Understanding these risk factors is essential for both diagnosis and coding accuracy.
Gout ICD 10 in the Context of Revenue Cycle Management
Accurate Gout ICD 10 coding plays a crucial role in revenue cycle management in healthcare, ensuring proper reimbursement and compliance for healthcare providers. When gout is diagnosed, the correct ICD-10 code, such as M10.0 or M10.2, must be assigned to prevent claim denials and delays in payment. A professional medical billing company helps ensure these codes are applied correctly, streamlining the billing process and improving cash flow. By incorporating accurate coding into the revenue cycle, healthcare providers can avoid costly billing errors, maintain compliance, and receive fair compensation for services rendered, ultimately optimizing their financial operations.
Incomplete or incorrect coding can lead to:
- Denied Claims
- Delayed Reimbursements
- Audit Risks
- Lost Revenue Opportunities
Coders working with providers or through a medical billing company must ensure all clinical details are captured to avoid under- or over-coding.
Best Practices for Documenting Gout Diagnoses
To select the right Gout ICD 10 code:v
- Identify the exact joint affected (e.g., toe, knee, elbow)
- Specify laterality (right, left, bilateral)
- Determine if the condition is acute or chronic
- Note underlying causes (e.g., renal failure, medication, diet)
This level of detail supports proper selection from the M10 series.
Importance of Accurate Gout Coding in Medical Coding Compliance
For those managing or auditing healthcare claims, especially in medical coding, specificity in gout documentation supports:
- Clean Claims Submission
- Reduced Audit Risk
- Improved Compliance with Payers
- Optimized Reimbursement
Common coding errors include using unspecified codes, missing laterality, or confusing gouty arthritis with rheumatoid arthritis.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Coding Gout
- Using M10.9 unnecessarily – Always aim for more specific codes.
- Ignoring laterality – Most codes require left/right side documentation.
- Not checking for chronic kidney disease – This can change the code to M10.3.
- Mixing idiopathic and secondary gout – Determine root cause from documentation.
ICD-10 and EMR Tips for Providers
- Ensure gout symptoms and causes are well-documented during evaluation.
- Use EHR prompts to guide detailed input (side, type, duration).
- Verify medication lists potential drug-induced causes.
These practices help ensure the code selects the most appropriate ICD-10 code.
Conclusion:
Accurate Gout ICD 10 coding plays a critical role in ensuring correct diagnosis reporting, efficient billing, and strong revenue cycle performance. By understanding the different types of gout, their causes, and the importance of detailed documentation, healthcare providers and coders can minimize claim denials, improve compliance, and optimize patient care outcomes. Whether you’re working directly with a provider or through a medical billing company, mastering gout coding is an essential step toward seamless operations in medical coding and revenue cycle management healthcare. Stay proactive, document thoroughly, and ensure every case of gout is coded with the precision it deserves.
FAQs on Gout ICD-10 Coding
1. What does the ICD-10 code for unspecified gout?
M10.9 is the code for unspecified gout, but it should only be used if further detail is not available in the documentation.
2. When should I use M10.3 for renal impairment-related gout?
Use M10.3 when there’s clear documentation that gout is linked to kidney dysfunction or chronic kidney disease.
3. Can gout be coded without identifying a joint?
While you can use general codes, ICD-10 encourages documenting the specific joint affected (e.g., toe, knee).
4. Is laterality mandatory for Gout ICD 10 codes?
Yes. Indicating whether it’s left, right, or bilateral is necessary for compliance and claims processing.
5. How often should providers update their gout diagnosis documentation?
At every encounter involving joint pain or flare-ups. It ensures current, accurate, and payable coding.
Final Thoughts on Accurate Gout ICD 10 Documentation
Using the right Gout ICD 10 code doesn’t just support medical accuracy, it ensures billing success and patient care quality. Whether you’re in a clinical role or work with a medical billing company, it’s essential to stay current with the best practices in medical coding and revenue cycle management healthcare.







