Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is one of the most common heart conditions today, making accurate diagnosis and reporting essential for healthcare. That’s where CAD ICD-10 coding becomes crucial. Whether you’re a medical provider, coder, or billing expert, understanding the correct ICD-10 code for coronary artery disease helps ensure precise documentation, better treatment plans, and smooth insurance reimbursements.
In this guide, we’ll dive deep into everything you need to know about CAD ICD-10, including key codes, documentation tips, and why accuracy matters.
What is Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)?
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) — also referred to in medical coding as coronary artery disease ICD-10 code conditions — occurs when plaque builds up in the coronary arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle. This restriction can lead to:
- Chest pain (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Heart attacks (myocardial infarctions)
- Heart failure
- Irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias)
Understanding the seriousness of CAD is essential, both clinically and administratively, because it impacts how we code it using systems like ICD-10 for CAD.
You can also check out our services for: Medical billing services for small practices
What is the ICD-10 Code for Coronary Artery Disease?
The most commonly used ICD-10 code for coronary artery disease without any complications is:
I25.10 — Atherosclerotic heart disease of native coronary artery without angina pectoris
However, depending on the patient’s symptoms, history, and whether grafts are involved, there are multiple CAD codes you must know.
Common CAD ICD-10 Codes You Should Know
Here’s a table summarizing key CAD ICD-10 codes:
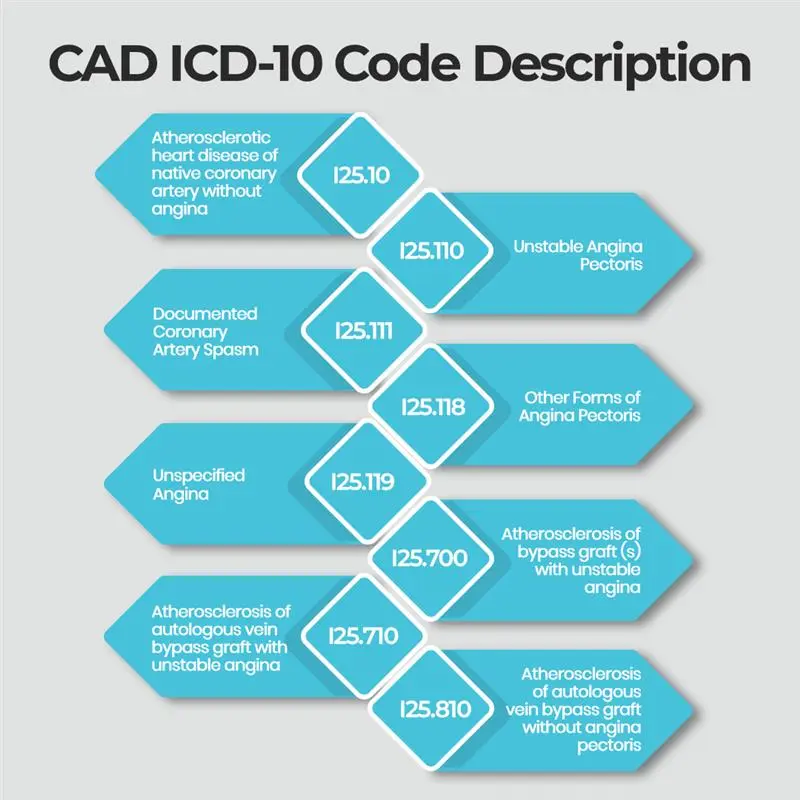
Important: Always base your code choice on detailed medical documentation. If you’re searching for “ICD 10 for CAD” — this chart gives you the right starting point.
How to Document CAD Correctly for ICD-10 Coding
High-quality documentation is crucial for selecting the correct CAD ICD code 10. Here’s what should be included:
- Type of coronary artery involved: native artery vs. graft
- Presence and type of angina: stable, unstable, or variant
- History of bypass surgery or stent placement
- Associated complications: like heart failure or prior myocardial infarction
Without these details, you risk coding errors that could delay treatment or impact insurance reimbursements.
Why Accurate CAD ICD-10 Coding Matters
Choosing the right ICD 10 code for CAD benefits not just the billing department, but the entire healthcare process.
1. Better Clinical Outcomes
Precise coding ensures the patient receives the right care pathways for their condition.
2. Accurate Billing and Reimbursement
Insurance companies rely on ICD-10 codes for claims processing. Incorrect CAD codes can lead to claim denials or revenue loss.
3. Compliance and Audit Readiness
Following the correct coronary artery disease ICD-10 code standards protects healthcare providers during audits and regulatory reviews.
4. Valuable Data for Research
Large-scale health data trends for coronary artery disease depend on correct coding at the individual level.
Practical Example: CAD ICD-10 Code Selection
Example:
A 68-year-old patient presents with atherosclerotic heart disease and reports unstable angina symptoms.
- Diagnosis: CAD with unstable angina
- Correct ICD-10 Code: I25.110
- If the patient had no angina, the proper code would be I25.10 instead.
CAD vs. Related Cardiac Conditions
When coding CAD, it’s important to distinguish it from similar or related conditions:
- CAD vs. Heart Attack (MI): A heart attack is often a complication of CAD but has its own set of ICD-10 codes.
- CAD with Heart Failure: Document and code both conditions separately if both are present.
- CAD in Bypass Grafts: Codes differ based on whether disease affects a bypass graft or a native artery
Understanding the nuances helps prevent coding errors when using ICD-10 for CAD and related heart conditions.
Quick Tips for Correct CAD Coding
- Always clarify the presence and type of angina.
- Identify if disease affects native arteries or grafts.
- Confirm any history of coronary interventions.
- Never guess — query providers if documentation is unclear.
- Stay updated with annual ICD-10 code updates.
Whether you type “CAD ICD code 10” or “ICD 10 code for coronary artery disease” into your coding software, accuracy is non-negotiable!
Conclusion
Mastering CAD ICD-10 coding ensures better healthcare delivery, accurate insurance billing, and meaningful clinical data reporting. Whether you’re coding ICD 10 CAD for a simple case without angina or handling complex cases involving bypass grafts, staying detail-oriented is key.
Always remember: the more accurate your ICD 10 code for CAD, the smoother the patient journey, billing, and compliance processes will be.
FAQS (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What is the ICD-10 code for CAD?
The primary ICD 10 code for coronary artery disease (CAD) without angina is I25.10.
2. How do you code CAD with unstable angina?
For CAD with unstable angina, the correct code is I25.110.
3. Is there a different ICD-10 code for CAD affecting bypass grafts?
Yes. If CAD affects bypass grafts, codes like I25.700 or I25.710 are used instead of I25.10.
4. Why is CAD ICD-10 coding important?
Accurate CAD ICD 10 coding ensures correct treatment, insurance reimbursement, and compliance.
5. Can CAD and heart failure be coded together in ICD-10?
Yes, both conditions must be documented and coded separately under ICD-10 for CAD and heart failure codes.







