Navigating the complexities of medical billing requires a clear understanding of how modifiers impact coding accuracy and reimbursement. Among the most frequently misunderstood is modifier 25, used to indicate that a significant and separately identifiable Evaluation and Management (E/M) service was provided on the same day as another procedure. Knowing the correct modifier 25 description is vital to avoid denials and ensure fair compensation. In this blog, we’ll break down how and when to use modifier 25, highlight common mistakes, and show how an optimized medical billing service can help practices maintain compliance and strengthen revenue integrity.
What Is Modifier 25?
Modifier 25 is appended to an E/M service code to indicate that the patient’s condition required a significant and separately identifiable E/M service, in addition to another service or procedure on the same day.
In simpler terms, it allows providers to be reimbursed for both the E/M service and the procedure, as long as the services are truly distinct and not bundled.
CPT Definition:
Modifier 25: Significant, separately identifiable evaluation and management service by the same physician or other qualified health care professional on the same day of the procedure or other service.
When Should You Use Modifier 25
Appropriate Scenarios Include:
- A patient visits for a new rash, and the physician also performs a skin biopsy.
- An established patient has a preventive visit and reports acute symptoms requiring additional evaluation.
- A physician evaluates a knee injury and also performs a joint aspiration.
To determine whether you should apply modifier 25, ask:
- Is the E/M visit medically necessary?
- Is it documented?
- Is it unrelated to the planned procedure?
Common Misconceptions and Errors
Using modifier 25 incorrectly can lead to audits or denials. Here are common mistakes:
- Appending it to non-E/M services – Modifier 25 is only for E/M services.
- Using it for pre-operative clearance – Unless distinct evaluation is needed, it’s bundled.
- Poor documentation – Lack of detailed notes that support a separate E/M service.
By avoiding these mistakes and adhering to the correct modifier 25 description, practices can remain compliant and efficient.
Benefits of Proper Modifier 25 Use
Correct use of modifier 25 ensures:
- Accurate billing and reimbursement
- Avoidance of claim denials
- Improved practice cash flow
- Compliance with CMS and private payer guidelines
If you’re managing a growing practice, integrating Revenue Cycle Management solutions like Precision Hub’s can help standardize the use of modifiers, improve coding accuracy, and prevent underbilling.
Do I Need Modifier 25?
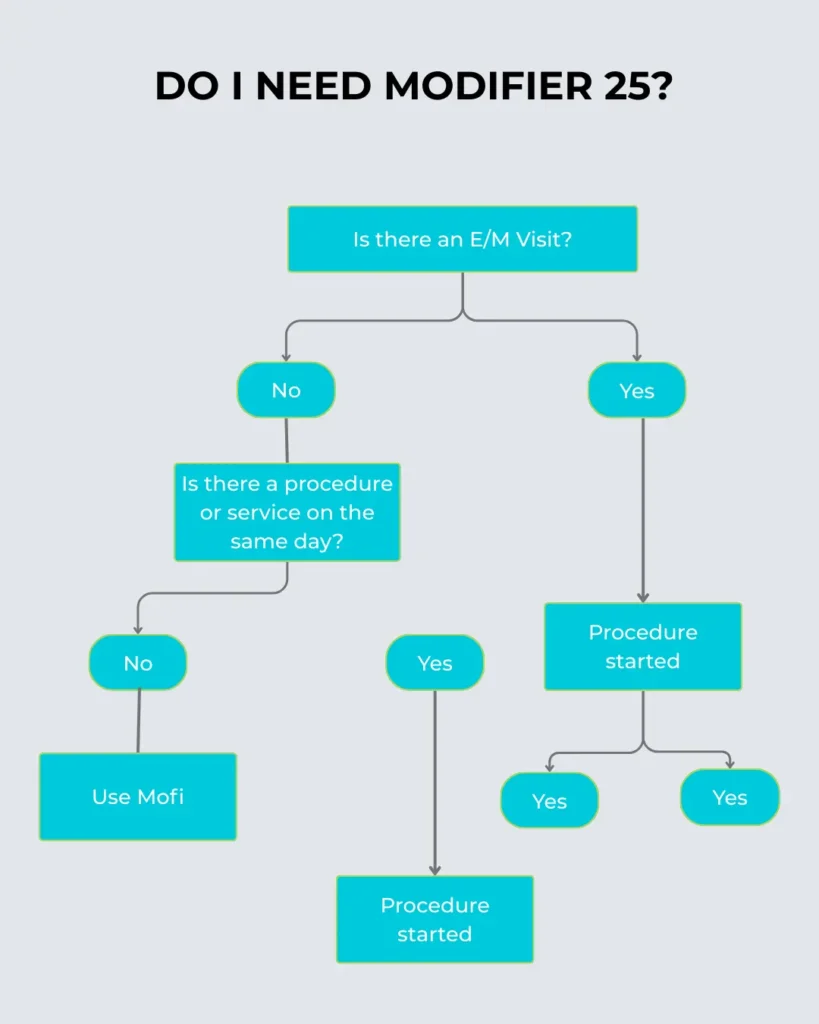
The result tells the coder whether to use modifier 25.
Documentation Is Key
To properly apply modifier 25, your documentation must:
- Separate the E/M from the procedure.
- Include patient complaints, history, exam, and medical decision-making.
- Show medical necessity for both services.
Failure to provide strong documentation is the leading reason for claim denials when modifier 25 is used.
Auditing and Compliance Considerations
Healthcare audits increasingly focus on modifier 25 usage due to frequent misuse. It’s critical for practices to:
- Conduct internal audits regularly.
- Use certified coders to verify claims.
- Stay updated on payer-specific guidelines.
Our medical billing and coding services at Precision Hub ensure your team is always in line with compliance standards, minimizing audit risks.
“Top 5 Reasons Claims with Modifier 25 Get Denied”

Integrating Modifier 25 Into Your Workflow
You can streamline modifier usage by:
- Educating staff on the modifier 25 description
- Including it in coding checklists
- Using software that flags missing documentation
- Partnering with a trusted medical billing service like Precision Hub
Consistency and accuracy can lead to better reimbursement and fewer rejected claims.
“How Modifier 25 Fits in Revenue Cycle Management”
- Patient Visit
- Documentation
- Modifier Decision
- Claim Submission
- Payment Processing
- Denial Management (if applicable)
Place modifier 25 at the center, showing its impact at every stage.
Conclusion
Mastering the correct use of modifier 25 is essential for any healthcare provider aiming to ensure accurate reimbursement and maintain billing compliance. This modifier plays a crucial role when multiple services are rendered on the same day, but only if applied correctly, with supporting documentation and a clear distinction between the E/M visit and the procedure. Misuse can lead to costly claim denials and increased audit risk.
By thoroughly understanding the modifier 25 description, training staff, and leveraging robust coding strategies, medical practices can streamline their billing process. Collaborating with a trusted partner like Precision Hub for your medical billing service, Revenue Cycle Management, and medical billing and coding needs ensures accuracy, efficiency, and compliance every step of the way.
Ultimately, using modifier 25 effectively not only safeguards revenue but also supports the sustainability and integrity of patient care operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can modifier 25 be used with any CPT code?
No. Modifier 25 should only be appended to E/M codes (typically 99201–99499) when there is a separate procedure or service on the same day.
Read more about: What are the CPT Codes for Urgent Care?
2. Does documentation need to support both services?
Yes. Payers require clear and complete documentation for both the E/M and the procedure. Without it, claims are likely to be denied.
3. Can I use modifier 25 on a preventive visit?
Yes, but only if a significant, separately identifiable problem-oriented E/M service is performed during the same visit.
4. What if the procedure was planned?
Then modifier 25 should not be used, as the E/M would be considered bundled and not distinct.
5. How can I reduce denials related to modifier 25?
Educate staff, improve documentation, and consider outsourcing to professional coders through a trusted medical billing and coding service







