Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep can have a significant impact on both a person’s well-being and daily activities. Insomnia affects millions of people and often necessitates professional treatment and thorough documentation. For healthcare providers and billing teams, it’s crucial to understand how to correctly code insomnia using ICD-10 guidelines to ensure proper care and timely reimbursement. In this guide, we’ll explore the key symptoms, diagnostic steps, and billing best practices for insomnia.
Whether you’re involved in medical billing and coding or seeking to improve your clinic’s processes, the information below will help you code and bill for insomnia correctly and efficiently.
What is Insomnia?
Insomnia is a common disorder that affects a person’s ability to fall asleep, stay asleep, or get restful, quality sleep. It can be short-term (acute) or long-lasting (chronic), and it impacts overall health, mood, and productivity. Chronic insomnia can often lead to secondary complications such as depression, anxiety, and even physical ailments like chronic pain.
The symptoms of insomnia vary, but they commonly include:
- Difficulty falling asleep at night
- Waking up frequently during the night
- Waking up too early in the morning, unable to fall back asleep
- Not feeling refreshed after sleep
- Daytime fatigue or sleepiness
- Poor concentration or memory issues
- Mood disturbances such as irritability, depression, or anxiety
While insomnia can occur on its own as a primary disorder, it can also be secondary to other medical conditions. For example, chronic pain, anxiety, depression, and even certain medications can all contribute to sleep disturbances. Therefore, proper diagnosis and accurate coding are critical to addressing the root causes and ensuring the right treatment approach.
ICD-10 Codes for Insomnia
Choosing the correct ICD-10 code for insomnia depends on the underlying cause, as well as the specifics documented in the patient’s chart. The ICD-10 coding system includes several codes related to insomnia, each used for different types of the disorder. Below are the main ICD-10 codes you may encounter:
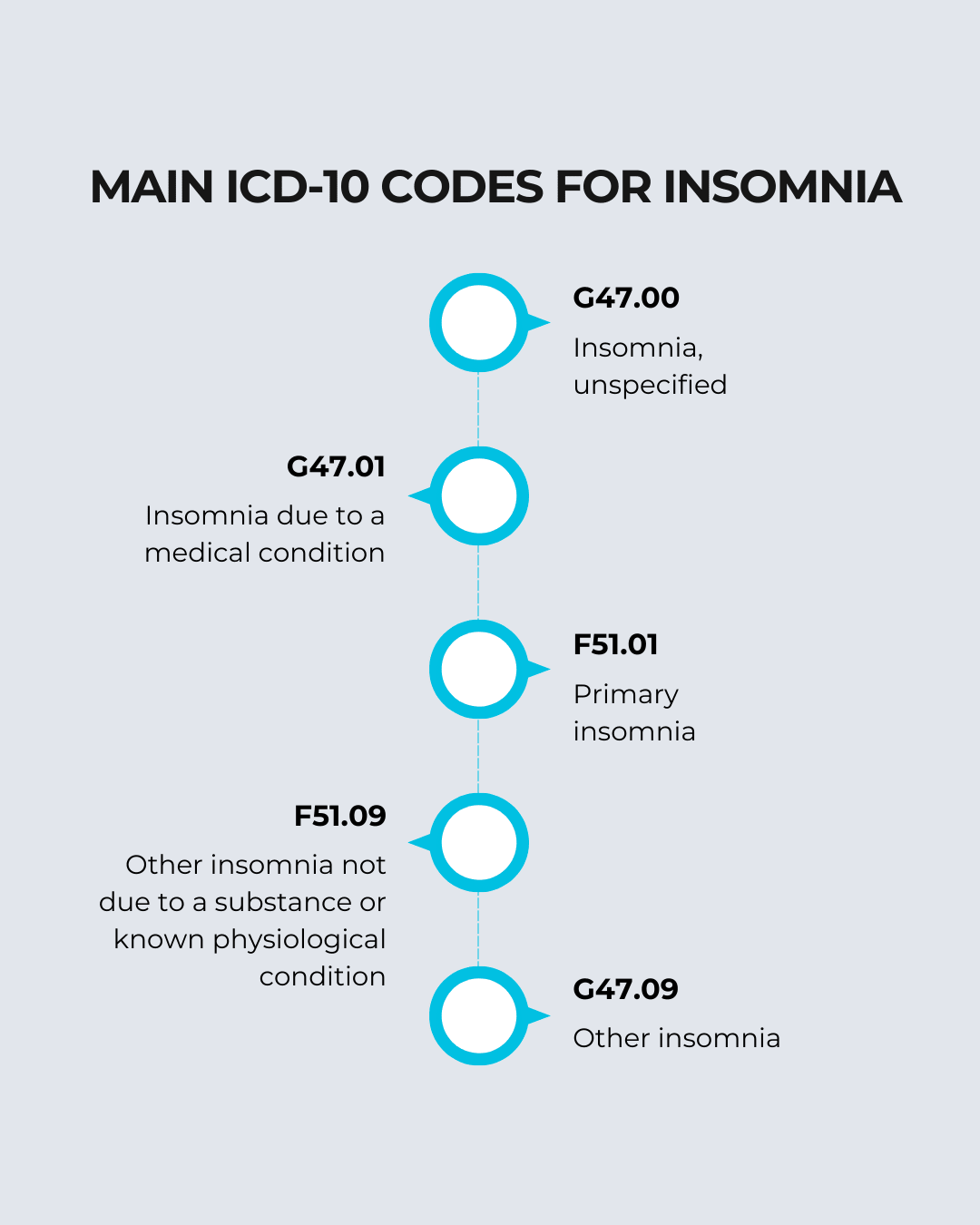
Quick Tips for ICD-10 Coding:
Get a fast overview of essential ICD-10 codes for accurately documenting insomnia. These quick tips help ensure correct coding, reduce errors, and support smoother billing processes.

By using the correct ICD-10 code, healthcare providers can enhance the accuracy of patient records, minimize claim rejections, and create a smoother billing workflow.
Proper Diagnosis of Insomnia
Accurate diagnosis is the foundation of successful insomnia treatment and effective medical billing. When diagnosing insomnia, healthcare providers must document several key factors to support the appropriate ICD-10 code. Thorough documentation ensures that the claim is backed up with sufficient medical information and that ( RCM ) processes run smoothly.
Key points to document include:
- Symptom history: Detailed information about the onset, duration, severity, and frequency of the insomnia symptoms.
- Impact on daily life: Describe how the lack of sleep affects the patient’s daily activities, including work, school, relationships, mood, and physical health.
- Contributing factors: Identifying any medical, psychological, lifestyle, or environmental factors that may contribute to the insomnia, such as a history of depression or chronic pain.
- Differential diagnosis: It’s essential to rule out other conditions that may cause similar symptoms, such as sleep apnea, narcolepsy, or restless leg syndrome.
- Response to interventions: Document what treatments the patient has tried, including medications and therapies, and their outcomes.
Accurate and detailed documentation not only leads to better patient care but also supports cleaner claims, reducing the chance of delays or denials in the billing process.
Billing Guidelines for Insomnia
Once the correct ICD-10 code has been selected, it’s time to focus on the billing aspect. Billing for insomnia treatment involves selecting the appropriate CPT codes and following payer-specific guidelines.
1. Pair ICD-10 Codes with Appropriate CPT Codes
When treating insomnia, different services are provided depending on the nature of the treatment. For example, counseling, psychotherapy, and sleep studies each require specific CPT codes. Here are some common CPT codes used for insomnia treatment:

Proper alignment between ICD-10 and CPT codes ensures that services are billed correctly and that the practice remains compliant with healthcare billing standards.
2. Link Services to Medical Necessity
It’s essential to demonstrate that the provided services are medically necessary. Documentation should outline how each treatment or diagnostic test directly addresses the patient’s insomnia symptoms and needs. This is a crucial step for ensuring insurance companies approve the treatment and that reimbursement occurs without delay.
3. Follow Payer-Specific Rules
Different insurance companies may have varying requirements when it comes to insomnia-related treatments. Some services, like cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), may require prior authorization before treatment begins. It’s essential to verify these payer-specific guidelines to avoid claim rejections or delays.
4. Code Comorbidities
In many cases, insomnia may be secondary to other health conditions such as depression, anxiety, or chronic pain. It’s vital to code for these comorbid conditions as well, as this helps reflect the full complexity of the patient’s health status. Accurate coding of comorbidities helps strengthen claims and provides a clearer picture of the patient’s overall health.
Following these billing guidelines helps providers reduce delays, avoid claim issues, and keep operations running smoothly.
Common Mistakes in Insomnia Coding and Billing
Despite best efforts, common mistakes in insomnia coding and billing can still occur. Here are a few to watch out for:
- Using unspecified codes: It’s important to use the most specific code available. Using G47.00 when more specific options like G47.01 or F51.01 exist can result in claims being rejected.
- Omitting secondary diagnoses: If insomnia is caused by another condition, both the insomnia code and the secondary condition must be included in the claim.
- Misaligned CPT/ICD-10 pairings: Incorrectly pairing CPT codes with ICD-10 codes can lead to denials. For example, billing a sleep study with an unspecified insomnia code might not meet the criteria for reimbursement.
- Inadequate documentation: Poor or incomplete documentation can make it difficult to justify the services provided, leading to delays or denials in reimbursement.
Partnering with a professional medical billing service can help healthcare providers avoid these common pitfalls and ensure their billing practices are streamlined and efficient.
Treatment Approaches for Insomnia (And Coding Considerations)
The treatment approach for insomnia depends on its underlying cause and severity. The following strategies are commonly employed:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I): This therapy focuses on changing the behaviors and thoughts that contribute to insomnia. It’s often a first-line treatment, especially for primary insomnia.
- Sleep hygiene education: This involves teaching patients about healthy sleep habits and lifestyle changes that promote better sleep.
- Medication: Pharmacologic treatment may include hypnotics or sedatives to help with sleep onset or maintenance.
- Relaxation techniques: Techniques like deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce stress and promote better sleep.
- Addressing underlying conditions: If insomnia is secondary to conditions like depression or chronic pain, those conditions should be treated concurrently.
Each treatment approach can involve specific CPT codes. For example, CBT-I typically involves multiple therapy sessions, each billed under psychotherapy codes. Sleep studies, on the other hand, require specific codes like 95810 for overnight testing.
Accurately linking the insomnia diagnosis with related treatment services ensures compliance with medical billing and supports efficient reimbursement.
Conclusion
Accurate insomnia ICD-10 coding is more than just a billing requirement — it’s an essential part of providing excellent patient care, maintaining regulatory compliance, and improving practice profitability. By properly diagnosing insomnia, documenting thoroughly, selecting the correct codes, and aligning treatment services, healthcare providers can avoid common billing errors and maintain smooth operations.
FAQS (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What is the ICD-10 code for unspecified insomnia?
G47.00 is used when no specific cause for insomnia is documented.
2. When should I use G47.01?
Use G47.01 when insomnia is linked to a medical condition like asthma or chronic pain.
3. How do I code primary insomnia?
Use F51.01 for insomnia not caused by another health issue.
4. What if the insomnia doesn’t fit standard categories?
Use F51.09 or G47.09 for insomnia that doesn’t align with specific causes.
5. Why is accurate insomnia coding important?
It helps reduce claim denials, ensures faster payments, and keeps patient records accurate.







